LAGOS, MARCH 2, 2018 – The spring in the step of Nigeria’s economy is likely to show up in the results of the country’s banks when they start reporting 2017 earnings from this month.
Record high interest rates of 14 percent since July 2016 means there is no shortage of yield for banks, many of which parked their funds to profit from the safety of Treasury bills and other fixed-income securities rather than lending, where there is more risk.
A drop in those yields from a record highs in August means that 2018 will be more challenging for lenders, despite the positive macro backdrop, according to Ogunsanya and Stermer. Volatility in foreign-exchange related gains, limited scope for cost efficiencies and rising political risks before elections in early 2019 also cloud the outlook for this year, the RenCap analysts said.
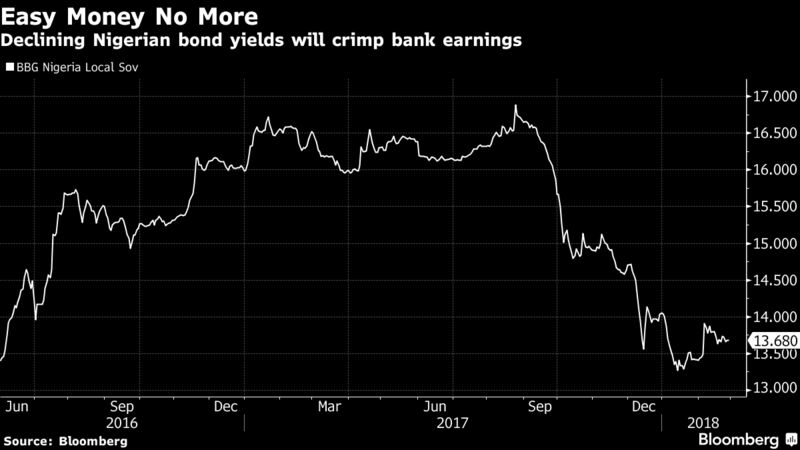
Lenders Lending
Banks will be able to close the revenue gap created by declining interest rates by lending more into a strengthening economy, according to Stanbic IBTC Holdings Plc analyst Muyiwa Oni. Some banks may boost loan growth to 15 percent this year compared with 10 percent in 2017, he said.
“Credit growth will be a big driver” in 2018, Oni said. While lower rates may reduce the cost of funding for banks, net interest margins may still narrow by anything from 100 basis points to 200 basis points this year, he said.
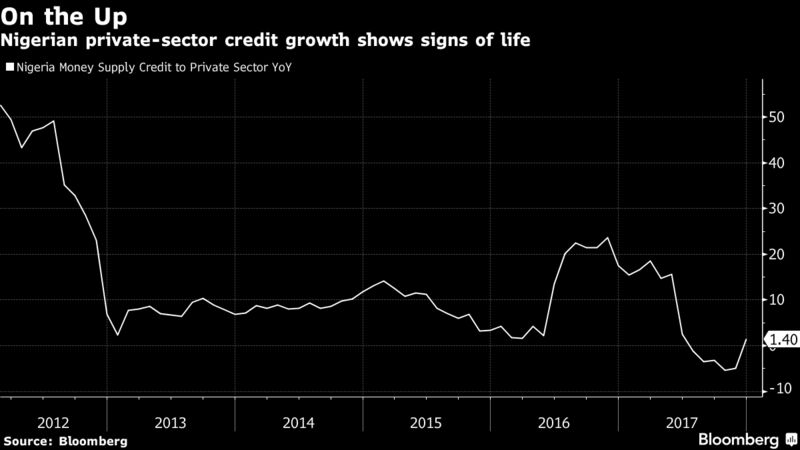
Fewer Sour Loans
The recession in 2016 hampered the ability of companies to meet their obligations to lenders, prompting a surge in bad debts. Non-performing loans as a percentage of overall credit peaked at 26 percent for FBN Holdings Plc, the country’s largest lender by revenue. NPLs will continue to trend downward after improving to 20 percent in the nine months through September, Adesola Adeduntan, the chief executive officer of FBN’s First Bank of Nigeria, said on Feb. 22.
An improvement in operating conditions, the restructuring of loans, recoveries and some write-offs will see the pace of unpaid loans ease into 2018, Fitch Ratings said in October.
Capital Challenges
At least three small- to medium-sized banks will run into difficulties with their capital levels this year and will need to raise cash, said Robert Omotunde, the head of investment research at Afrinvest West Africa Ltd., without naming the lenders. “A lot of tier two banks have issues with NPLs and it’s eating into their capital buffers.”
Stanbic IBTC’s Oni predicts that the capital adequacy ratio across the industry will probably drop by 100 to 200 basis points, mainly because of the introduction of IFRS 9 reporting standards, which will require higher provisioning.
Bigger lenders including Zenith Bank Plc, United Bank for Africa Plc and Access Bank Plc were able to raise funding in the Eurobond market last year, while smaller ones struggled to boost their buffers. Stress tests showed that the capital adequacy ratio across the banking industry worsened to 12.8 percent in April from 13.6 percent in February, according to the central bank.
Taking Stock
There is still some room for shares to rally even after the Nigerian Stock Exchange Banking 10 Index surged by a record 73 percent in 2017, according to Lekan Olabode, a bank analyst at Vetiva Capital Management Ltd. in Lagos, although the pace won’t match that seen last year. Smaller lenders may also show faster earnings growth and biggest share-price gains.
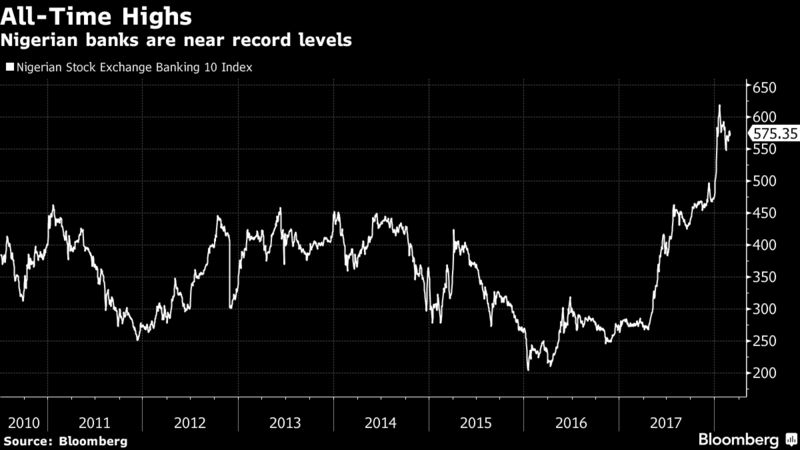
“The banking sector is significantly undervalued,” he said. “This year, it is the small banks that we expect to do more.”









